Building Trust in Geospatial Data: A Customer Driven Data Quality Feedback Mechanism for GDI
-
CDPG
-
February 9, 2026
-
Blog
-
0 Comments
When shopping online, we rely on product reviews to make informed purchasing decisions. A 4-star rated laptop with hundreds of user reviews gives us confidence about its performance, while a restaurant with consistent positive feedback becomes our go-to choice for dining. But what if the same principle could be applied to geospatial data? This is precisely what the Integrated Geospatial …
Continue Reading
AI and the Future of Geospatial: Transformation, Not Replacement
-
CDPG
-
December 11, 2025
-
Blog
-
0 Comments
Summary of Keynote Talk by Peter Rabley, CEO, Open Geospatial Consortium: “Will AI Eat Geospatial?” With the advent of Generative AI, a question that intrigues the mind of the Geospatial community across the globe is “Will AI eat geospatial?” With rapid advances in this ‘more than disruptive’ technology that is artificial intelligence, many wonder whether traditional geospatial roles and processes …
Continue Reading
Integrating Spatial Analytics and Routing Algorithms for Flood Response: The FIRS Approach
-
CDPG
-
December 11, 2025
-
Blog
-
0 Comments
Every monsoon, India braces itself for one of its most persistent natural hazards: flooding. It is driven by intense monsoons, cyclones, tsunamis, or earthquake-damaged dams failure causing extensive loss of life, infrastructure damage, and long term economic disruption. According to the National Flood Commission (1980), about 0.4 million km² of India’s area is affected by floods annually, including 0.037 million …
Continue Reading
Breaking Data Silos: How GDI is Transforming Access to Geospatial Information in India
-
CDPG
-
November 5, 2025
-
Blog
-
0 Comments
For years, some of India’s most valuable geospatial datasets remained scattered across government departments, research institutes, or private organizations. They held immense potential to transform logistics, strengthen climate resilience, and support smarter urban planning, but they remained difficult to access, buried in different formats and lacking interoperability. Recognizing this challenge, the Government of India through the Department of Science and …
Continue Reading
GDI federated node: Smarter way of sharing your data without giving it away!
-
CDPG
-
November 5, 2025
-
Blog
-
0 Comments
Introduction Traditionally, data exchanges have relied on a centralized architecture — where both the control plane (responsible for cataloging, authorization, and access management) and data plane (where the datasets are stored and served) are hosted centrally. While functional, this model faces challenges of scalability, data governance, and security risks, especially as data volumes and contributors grow. The GDI federated architecture …
Continue Reading
An Overview of the GDI Python SDK
-
CDPG
-
April 17, 2025
-
Blog
-
0 Comments
The GDI Python SDK is a command-line toolkit designed to streamline interaction with the Integrated Geospatial Data Sharing Interface (GDI), accessible at https://catalogue.geospatial.org.in. Built to support a wide range of geospatial workflows, the SDK enables users to efficiently access, process, and manage both vector and raster data within a unified, scriptable environment. With support for various storage backends including MinIO, …
Continue Reading
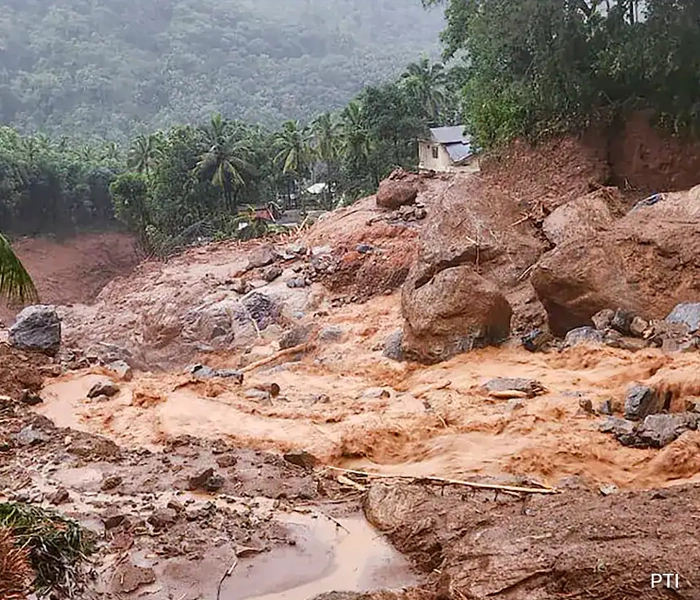
Landslide Damage Assessment, Wayanad, Kerala
-
CDPG
-
April 8, 2025
-
Blog
-
0 Comments
India is experiencing various forms of natural hazards including, earthquakes, landslides, floods, forest fires, cyclones, and drought etc. Among these, landslides are one of the more prominent and devastating natural hazards especially in the hilly areas of the country. The eastern part of Kerala state (Western Ghats) in southern India is highly prone to landslides due to its Physio‐climatic condition, …
Continue Reading
From Space to Soil: Leveraging Satellite and Weather Data for Flood Damage Assessment and Insurance Claims for Farmers
-
CDPG
-
April 8, 2025
-
Blog
-
0 Comments
In an era where climate change is bringing more erratic weather patterns, the consequences of heavy rainfall and flooding on agriculture can be devastating. Farmers, particularly those reliant on seasonal crops, are often left in precarious situations, struggling to recover from lost yields. In the early September of 2024, in NTR district of Andhra Pradesh, this harsh reality recently came …
Continue Reading
Assessment of Urban Heat Island (UHI) in Bengaluru Using Earth Observation Datasets.
-
CDPG
-
April 8, 2025
-
Blog
-
0 Comments
Rapid urbanisation causes several issues, including the Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect, where urban areas experience significantly higher temperatures than their rural surroundings. This is due to several factors associated with urbanisation, including the replacement of vegetation with buildings, roads, and other impermeable surfaces that absorb and retain heat. Additionally, heat emissions from industries and vehicles also contribute to the …
Continue Reading
Modelling Agricultural Land Suitability based on Soil Properties
-
CDPG
-
March 21, 2025
-
Blog
-
0 Comments
Suitability studies in Geographic Information Systems (GIS) play a vital role in spatial planning and resource management by assessing the appropriateness of a given area for specific land uses based on various criteria. These studies integrate multiple datasets and analytical techniques to evaluate how well certain locations meet predefined requirements, thus guiding decision-making in sectors such as agriculture, urban development, …
Continue Reading